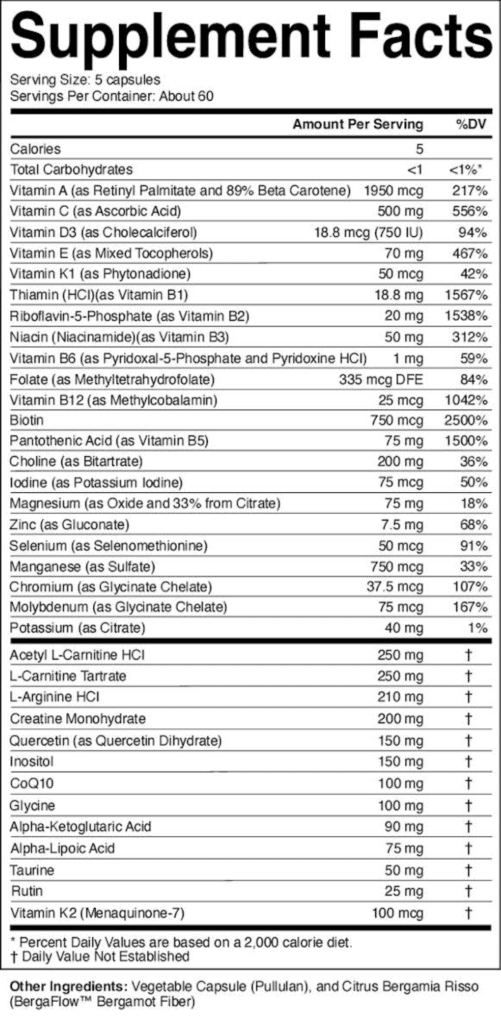
$84
ZINC
Zinc is a mineral that must be obtained in the diet and is required for life. Zinc is a cofactor necessary for the activity of about 100 enzymes, including those in energy metabolism, thyroid function, synapse formation, immune function, wound healing, and blood clotting. Zinc deficiency is both serious and common, especially occurring in individuals with poor nutrition and/or gastrointestinal disease. Zinc deficiency is often suspected due to disorders of the skin, nails, and hair. Other features include mental or cognitive disorders, sensory loss, frequent infections, mouth sores, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. Zinc is an agonist for (turns on) for GABA receptors, one of the chief inhibitory pathways in the nervous system, and an antagonist for (turns off) NMDA glutamate receptors, one of the chief excitatory pathways in the nervous system, which may play a role in neuroprotection. The combination can lead to abnormal inhibitory–excitatory balance, potentially promoting increased excitatory neurological processes, including autistic behaviors and possibly neurological regression. Zinc is often recommended for a variety of health conditions including conditions of the gastrointestinal, immunological, ocular, neurological, dermatological, and endocrine systems. Side effects can include nausea at the higher doses commonly used in supplementation.
Zinc in EnergyNeeds®
Zinc is added in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of zinc in energy metabolism, and its role in GABA and NMDA glutamate receptor activation. As the dose of zinc is moderate, side effects are unexpected.
Zinc is a mineral that must be obtained in the diet and is required for life.
Zinc is a cofactor necessary for the activity of about 100 enzymes. Thus, zinc has wide-reaching effects in the body, including in energy metabolism, thyroid function, synapse formation, immune function, wound healing, and blood clotting.
Zinc deficiency is a serious and common problem worldwide, affecting over 2 billion people. In addition to a common problem in the developing world, zinc deficiency is not rare in developed countries, especially in individuals with poor nutrition and/or gastrointestinal disease. Zinc deficiency is often suspected due to disorders of the skin (eczema, seborrhea, acne, Impaired wound healing), nails (brittle), and hair (thin, sparse). Other features include mental or cognitive disorders (include attention and mood), sensory loss (including blunted taste), frequent infections, mouth sores, diarrhea, and loss of appetite.
Zinc is often recommended for a variety of health conditions including growth retardation, gastrointestinal conditions (acute diarrhea, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcers), immunological conditions (frequent infections including the common cold, malaria, AIDS, asthma), eye diseases (macular degeneration, night blindness, cataracts), neurological disorders (Alzheimer, autism, ADHD, anorexia nervosa), dermatological conditions (psoriasis, eczema, acne, slow wound healing, hair loss), diabetes, and high blood pressure. Some athletes use zinc for improving athletic performance and strength.
Zinc is an agonist for (turns on) for GABA receptors, one of the chief inhibitory pathways in the nervous system, whereas under stimulation may lead to increased hyperactive behaviors in some individuals. Zinc is also an antagonist for (turns off) NMDA glutamate receptors, one of the chief excitatory pathways in the nervous system, which may play a role in neuroprotection and thus potentially guard against episodes of neurological regression. There is evidence of abnormal inhibitory–excitatory balance in the brain of individuals with some brain disorders, which may be targeted by therapy via effects on GABA and glutamate neurotransmission.
Studies performed to date, the clinical experience of many expert physicians, and the generally benign nature of zinc supplementation, have convinced some experts to offer zinc supplementation to their patients with a wide variety of disease manifestations. Individuals that are more likely to benefit are those who also suffer from chronic diarrhea, vision loss, mouth sores, disease of the skin, nails, and/or hair, frequent infections, reduced inhibitory–excitatory balance (anxiety, hyperactivity, impulsivity, OCD, “autistic” behaviors, etc.), or with a history of regression.
Zinc is considered to be likely safe at doses up to 40 mg a day in adults. Occasionally, nausea can occur at dosages commonly used for supplementation. Additional potential side effects are vomiting, diarrhea, and a metallic taste.
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a zinc deficiency, and this test is indicated in specific situations where zinc deficiency is likely or suspected.
The dose of zinc in EnergyNeeds® (15 mg in adults) is lower than that is some other products, mostly due to the occasional occurrence of nausea. Therapeutic dosages of zinc typically vary from 15 to 220 mg a day. Thus, you may wish to speak to your health care provider regarding additional zinc supplementation beyond EnergyNeeds® if you have one of the conditions for which higher dosing is often recommended.
How and why Zinc is used in EnergyNeeds®
Zinc is added to EnergyNeeds® in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of zinc in energy metabolism, its role in GABA and NMDA glutamate receptor activation, and because of the available data suggesting a possible role in the dietary supplementation of various conditions. While definitive large double-blind studies have not been performed to date, the multiple studies performed to date, the clinical experience of many physicians, and the generally benign nature of zinc supplementation, have convinced many experts to offer zinc supplementation to their patients with a variety of conditions. The dose of zinc in EnergyNeeds® (15 mg in adults) is lower than that is some other products, mostly due to the occasional occurrence of nausea. Side effects are unexpected at the doses used in EnergyNeeds®.
Order EnergyNeeds®Today
Formulations