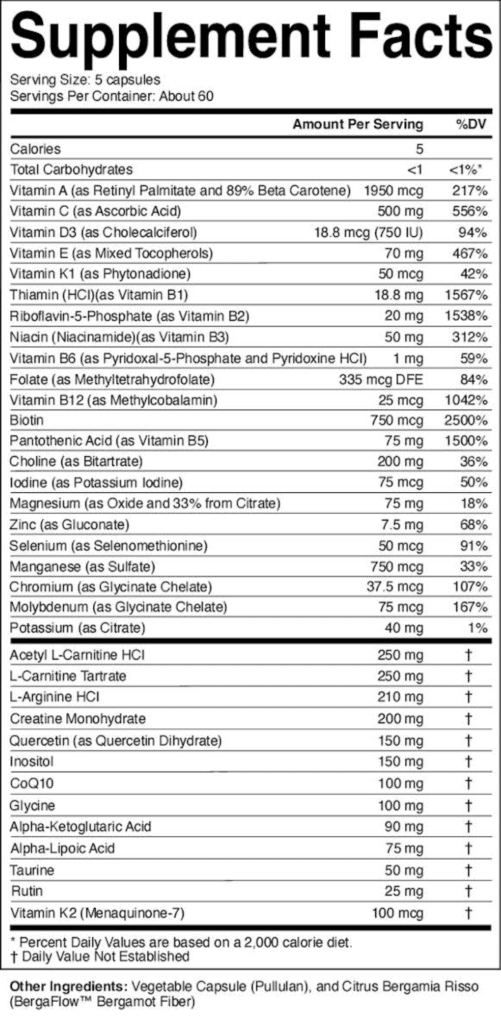
$84
Vitamin D (also known as vitamin D3 and cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin through a process that is dependent on sun exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Vitamin D is converted by the body to 25-hydroxyvitamin, which is measured in blood tests to determine vitamin D status, and then to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which is the biologically active form. Vitamin D circulates as a hormone in the blood, and has a major role in regulating calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, which have major impact on bone. In addition, vitamin D has several other effects, including on cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation, calcium signaling, brain development, neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions, neurotransmission, synaptic plasticity, neuromuscular and immune functions, reduction of inflammation, and regulation of gene expression. Deficiency of vitamin D is caused by inadequate sun exposure in conjunction with inadequate dietary intake. Deficiency is common even among individuals with light skin tones with the modern custom of extensive skin coverage by clothes and sunscreens, and increasingly sedentary, indoor lifestyles. Vitamin D is present in appreciable quantities in only a few foods, and supplementation is increasingly recommended. Vitamin D deficiency typically results in impaired bone mineralization, which leads to bone fractures and bone-softening diseases including osteomalacia in adults, and rickets in children. Thus, vitamin D is often used to treat bone-related conditions, although it is often recommended for many other conditions beyond the skeleton. While sun exposure is an excellent way to boast vitamin D levels, practical concerns and fear of cancer have led many to recommend supplementation. Vitamin D toxicity is very rare, even in studies using extremely high doses by injection, although levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D above 50 or 60 ng/ml may be too high. The vitamin D dose in EnergyNeeds® is only moderate, and side effects and/or levels > 50 ng/ml are unexpected. You may wish to speak to your physician regarding blood testing and potential additional vitamin D supplementation beyond that provided by EnergyNeeds®.
Vitamin D in EnergyNeeds
Vitamin D is added in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the multiple effects of vitamin D, including in nerve and immune function. Vitamin D requirements vary greatly among individuals, and the 1,500 IU (37.6 mg) present in EnergyNeeds may not be sufficient. You may wish to speak to your physician regarding blood testing and potential additional vitamin D supplementation beyond that provided by EnergyNeeds®.
While the term vitamin D refers to a group of fat-soluble steroids, the most important member of this group, and the one present in supplements, is vitamin D3 (also known as cholecalciferol), which is referred to herein as simply “vitamin D”. Vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin from cholesterol through a process that is dependent on sun exposure to ultraviolet (UV) B radiation. Vitamin D is converted in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D (also known as 25(OH)D), which is the compound measured in blood to determine a person’s vitamin D status. 25-OH-vitamin D is further converted by the kidneys to form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which is the biologically active form of vitamin D.
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (also known as calcitriol) circulates as a hormone in the blood, and has a major role in promoting the healthy growth and remodeling of bone. In particular, calcitriol increases intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, as well as being required for bone growth and remodeling by bone cells (osteoblasts and osteoclasts). Calcitriol also has several other effects, including on cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation, calcium signaling, brain development, neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions, neurotransmission, synaptic plasticity, neuromuscular activity, immune function, reduction of inflammation, and regulation of gene expression. Vitamin D regulates about 3% of all of the about 25,000 genes in humans, including activating the TPH2 gene that synthesizes tryptophan in the brain (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24558199).
Deficiency of vitamin D is caused by inadequate sun exposure in conjunction with inadequate dietary intake. Deficiency is increasingly common throughout the world. While often thought of as only a substantial issue in darker-skinned individuals, deficiency is common even among those the lightest skin tones with the modern custom of extensive skin coverage by clothes and sunscreens, and with increasingly sedentary, indoor lifestyles. As vitamin D is present in appreciable quantities in only a few foods, mostly oily fishes, supplementation is increasingly recommended. Of note, bowel disease can also predispose towards vitamin D deficiency by decreasing absorbance even when some supplementation is provided. Vitamin D deficiency typically results in impaired bone mineralization, which leads to bone fractures and bone-softening diseases including osteomalacia in adults, and rickets in children.
Vitamin D is used for preventing and treating rickets, weak bones (osteoporosis), bone pain, bone loss in people with hyperparathyroidism, and inherited disorders causing weak bones such as osteogenesis imperfecta. It is also used for preventing falls and fractures in people at risk for osteoporosis, and preventing low calcium and bone loss in people with kidney failure. In addition, vitamin D is sometimes used for many conditions beyond bones, including high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, muscle weakness, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, bronchitis, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), tooth and gum disease, vitiligo, scleroderma, and psoriasis. Multiple studies have shown efficacy in the treatment of autism. Furthermore, some use vitamin D for boosting the immune system, preventing autoimmune diseases, and preventing cancer.
Vitamin D is fat soluble, yet toxicity appears to be rare, even in studies using extremely high doses such as 150,000 IU/month by intramuscular injection. Some sources suggest that blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D above 50 or 60 ng/ml may be too high, and if present recommend reducing the amount of supplement provided (Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2010; https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional). Side effects are rare at usual doses used in supplementation. The vitamin D dose in EnergyNeeds® is only moderate, and side effects are not expected.
Blood testing of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is the best indicator of vitamin D status. Testing can be used to diagnosis deficiency as well as to monitor therapy, and is recommended by many experts.
There is a lot of controversy about what 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are ideal. While the Institute of Medicine (USA) stated in 2010 that levels above 20 ng/ml are adequate, most laboratories list above 30 ng/ml as “normal”, and some studies recommend levels above 40 ng/ml. Achieving the latter level may require doses of which many physicians are uncomfortable. Thus, the vitamin D dose in this product (1,500 IU in adults, 37.6 mg) is high, but not among the very high doses advocated by some experts. You may wish to speak to your physician regarding blood testing and potential additional vitamin D supplementation beyond that provided by EnergyNeeds®.
How and Why Vitamin D Is Used in EnergyNeeds®
Vitamin D is added to EnergyNeeds® in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given its roles in nerve and immune functions. While definitive large double-blind studies have not been performed to date, the multiple studies performed to date, the clinical experience of many physicians, the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the population, and the generally benign nature of vitamin D supplementation, have convinced many experts to offer vitamin D supplementation to their patients. Side effects and/or levels > 50 ng/ml are unexpected with the dose of vitamin D used in EnergyNeeds®.
Order EnergyNeeds®Today
Formulations