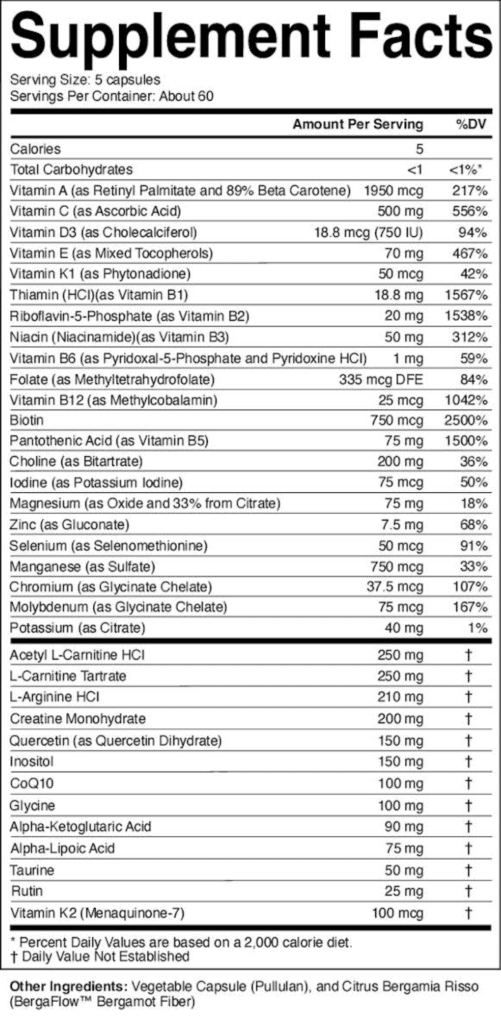
$84
FOLATE (ALSO KNOWN AS FOLIC ACID OR VITAMIN B9, INCLUDING VARIETIES OF ACTIVATED FOLATE, SUCH AS 5-METHYLTETRAHYDROFOLIC ACID, AND BRAIN-READY DERIVATIONS CALCIUM FOLINATE, AND FOLINIC ACID)
Folate, also known as folic acid or vitamin B9, is one of the eight B-complex vitamins. Folate cannot be manufactured by humans and is obtained exclusively from the diet. Folate is an enzyme cofactor for a wide range of enzymes, including enzymes in DNA and RNA synthesis. Folate also has important roles in DNA methylation, redox metabolism, and blood cell formation. Folate deficiency can present as fatigue, weakness, irritability, lethargy, headache, depression, palpitations, shortness of breath, constipation, frequent illness, mouth sores, and/or megaloblastic anemia. In addition to poor diet, gastrointestinal conditions, pregnancy, and certain genetic variants (SNPs, pronounced as “snips”) can predispose towards folate deficiency. Folate is widely prescribed to reduce the risk of birth defects, especially neural tube defects. In addition, folate is often recommended for a multitude of different diseases and situations. The inactivated form of folate that is present in foods and most food supplements must be activated in the body in order to have biological function. Activation is slow in humans, and highly variable between people based on the presence or absence of certain gene SNPs. Very high doses of inactivated folate can result in side effects in people with slowed activation. EnergyNeeds® is designed to limit side effects by only including activated folate at moderate dosing.
Folate in EnergyNeeds®
Folate, provided as activated folate (5-methyltetrahydrofolate), is added in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of folate in DNA synthesis, methylation, and energy metabolism. Side effects are unexpected with the type and dosing used in EnergyNeeds®.
Folate, also known as folic acid or vitamin B9, is one of the eight B-complex vitamins. Folate cannot be manufactured by humans and is thus a true vitamin, obtained exclusively from the diet.
Folate is an enzyme cofactor, which means that it is a necessary component for enzyme function. Folate is a cofactor in a wide range of enzymes, especially including enzymes in both DNA and RNA synthesis. Folate is also essential for DNA methylation, and thus has a critical role in gene expression (in determining which genes are activated). In addition, folate plays important roles in redox metabolism, and the formation of different types of blood cells.
Folate deficiency can present as fatigue, weakness, irritability, lethargy, headache, depression, palpitations, shortness of breath, constipation, frequent illness, mouth sores, premature greying hair, and/or megaloblastic (large red blood cell) anemia. In addition to poor diet, gastrointestinal conditions that affect vitamin absorption can lead to folate deficiency. In addition, some people have genetic variants that hinder the body in activating dietary folate. A developing fetus requires a lot of folate, and deficiency is relatively common during pregnancy.
Folate is widely prescribed before conception and in early pregnancy to reduce the risk of birth defects, especially neural tube defects. Folate is often recommended to reduce blood levels of homocysteine, in which high levels likely constitute an increased risk for heart disease. In addition, folate is sometimes recommended for patients with anemia, ulcerative colitis, liver disease, alcoholism, kidney dialysis, memory loss, autism, Alzheimer disease, age-related hearing loss, age-related macular degeneration, osteoporosis, restless leg syndrome, sleep problems, depression, nerve pain, muscle pain, AIDS, and vitiligo. Folate is also used to prevent certain types of cancer, decrease the risk for stroke or cardiovascular disease, reduce symptoms related to aging, and prevent side effects of treatment with some forms of chemotherapy.
The inactivated form of folate (generally referred to simply as “folate”) is the form supplemented in food and in most food supplement (“vitamin”) products. Folate must be activated by conversion in the liver to various derivatives of tetrahydrofolate by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) in order to have biological function as an enzyme cofactor. The activity of DHFR is unusually slow in humans compared to in other mammals, with substantial variation in enzymatic activity between different people based on the presence or absence of certain gene variants (including SNPs, pronounced as “snips”). EnergyNeeds® contains only activated folate in the form L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate, which does not require conversion.
Folate is a water-soluble vitamin and thus considered to be generally non-toxic. However, depending on the individual’s genetic markers, high doses of inactivated folic acid might cause abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, rash, sleep disorders, irritability, confusion, excitability, and other side effects. EnergyNeeds® is designed to limit side effects by only including activated folate at moderate dosing. In addition, a main argument against widespread high levels of folate supplementation in bread and other foods is that high folate levels can mask a vitamin B12 deficiency, and thus is recommended that vitamin B12 should be supplemented along with folate. EnergyNeeds® also contains high levels of vitamin B12.
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a deficiency of this nutrient, but is generally not likely to have clinically utility. Folate transporter autoantibodies can be measured in blood. Brain folate deficiency can be determined by cerebrospinal fluid measurement of activated folate, but this test requires a spinal tap.
Individuals with severe folate transporter deficiency, including those with folate transporter autoantibodies, develop brain folate deficiency. These individuals can be treated with folinate, which is a form of folate that can cross the blood-brain barrier to enter brain independent of the brain folate transporter. Brain folate deficiency can result in autism, seizures, and movement disorders, among other conditions. You may wish to speak to your physician regarding folinate supplementation.
How and Why is Folate (B9) Used in EnergyNeeds®
Folate is added to EnergyNeeds® in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of folate in DNA synthesis, methylation, and energy metabolism. EnergyNeeds® contains no inactivated folate, and instead contains moderate-dosing of activated folate in the form of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF). Vitamin B12 deficiency is prevented as this vitamin is also present in EnergyNeeds®. Side effects are rare with the type and dosing of folate used in EnergyNeeds®.
Order EnergyNeeds®Today
Formulations