$84
Vitamin K
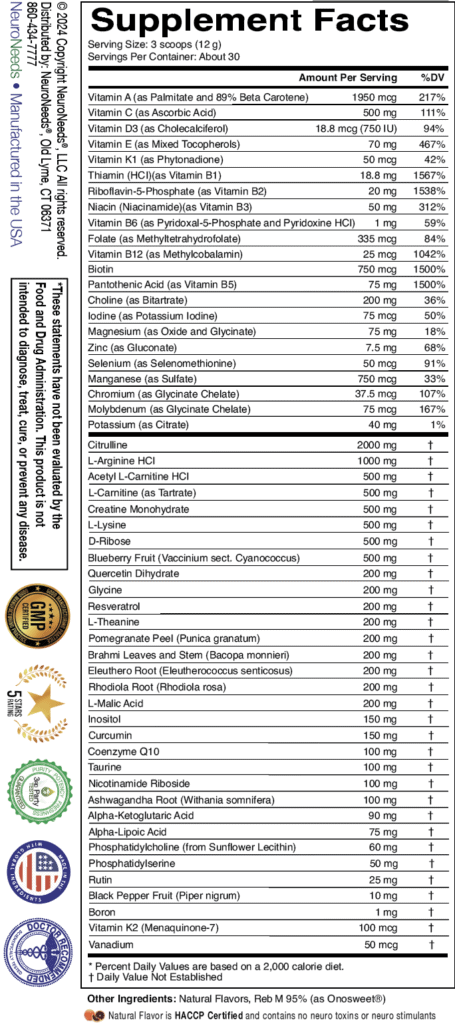
Vitamin K refers to a class of related compounds. Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) is found in plants and is the form generally found in dietary supplements. There are several forms of vitamin K2 (menaquinone), which are found at high amounts in certain animal and fermented products, yet is rarely found in dietary supplements. All forms are an enzyme cofactor for proteins that are needed for blood coagulation, and deficiency can lead to uncontrolled bleeding. Deficiency also can lead to osteoporosis and may promote calcification of arteries. Potential benefits include protecting brain functions such as thinking, learning, memory, and organizing. Vitamin K2, especially K2-7, is more bioavailable, remains in the body longer, and likely has more benefits than K1. Studies have shown that K2 may reduce the risk of death caused by coronary heart disease and certain types of cancer. ActivNeeds includes K1 and K2-7. Side effects are rare at doses used in ActivNeeds, although those on blood thinner medications should discuss vitamin K supplements with their health care practitioner before starting.
Vitamin K in ActivNeeds
Vitamin K is added to ActivNeeds in both the K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2-7 (menaquinone-7) in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of vitamin K1 in blood clotting and calcium utilization. Side effects are unexpected, although those on blood thinners should first consult their physician.
Vitamin K refers to a group of similar, fat-soluble, compounds. Vitamin K cannot be manufactured by humans and is thus a true vitamin, obtained exclusively from the diet. The term “vitamin K” refers to a class of related, naturally-occurring compounds: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2 (several forms of menaquinone, especially types 4 (K2-4) and 7 (K2-7). Of note, The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) does not distinguish between K1 and the many types of K2, all are counted as “vitamin K”. Vitamin K supplementation generally involves K1 (phylloquinone), which mostly comes from plant sources, such as leafy greens and blueberries. Humans can convert K1 to K2-4. Gut bacteria can convert K1 into K2-4 and other forms, including K2-7. Vitamin K2 is found in high amounts in certain animal-based (e.g., egg yolk, eel) and fermented (e.g., natto, kimchi, sauerkraut, blue cheese) foods. ActivNeeds® contains vitamin K in both the K1 and K2-7 forms.
Both forms of vitamin K have similar functions. Vitamin K is an enzyme cofactor for proteins that are needed for blood coagulation, in particular, factors II, VII, IX, and X, as well as proteins C and S. Vitamin K also assists in controlling the binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. Potential benefits include protecting brain functions such as thinking, learning, memory, and organizing.
Vitamin K2, especially K2-7, is absorbed more readily and is removed more slowly than is vitamin K1, and therefore the advantages are likely longer lasting. Some studies have suggested that vitamin K2 may be more effective at removing calcium than vitamin K1.
Vitamin K deficiency can develop in certain conditions, especially in severe gastrointestinal disease. In vitamin K deficiency, blood coagulation is impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Additionally, deficiency can lead to osteoporosis (weakened bones), and may promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.
Vitamin K is often supplemented in newborns, in individuals with liver or intestinal disease, and to reverse the blood thinning effects of the drug warfarin. Two studies found that vitamin K2 significantly reduced the risk of death from coronary heart disease (PMID: 15514282 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15514282, 19179058). One of those studies (PMID: 15514282 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19179058) showed a 50% reduction in such death on at least 32 mcg per day of K2. Some research suggests that vitamin K2 may reduce the risk of death caused by certain types of cancer. In women, vitamin K have been suggested to improve morning sickness, menopause, osteoporosis, and depression in those with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Despite being fat soluble, vitamin K is broken down very quickly, and rarely reaches toxic levels even with high intakes. Side effects are rare at doses in ActivNeeds. Those on blood thinner medications should discuss vitamin K supplements with their health care practitioner before starting.
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a deficiency of this nutrient, but is generally not likely to have clinically utility.
How and Why Vitamin K Is Used in ActivNeeds
Vitamin K is added to ActivNeeds in both the K1 and K2-7 forms in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, particularly in regard to the importance of vitamin K for the health of the blood, blood vessels, bone, and brain. While definitive large double-blind studies are few, the studies performed to date, the clinical experience of many physicians, and the generally benign nature of vitamin K supplementation, have convinced many experts to offer supplementation to their patients, especially with the more bioactive and longer lasting form of K2-7. Side effects are rare at doses in ActivNeeds, although those on blood thinners should first consult their physician.
Order ActivNeeds Today
Formulations