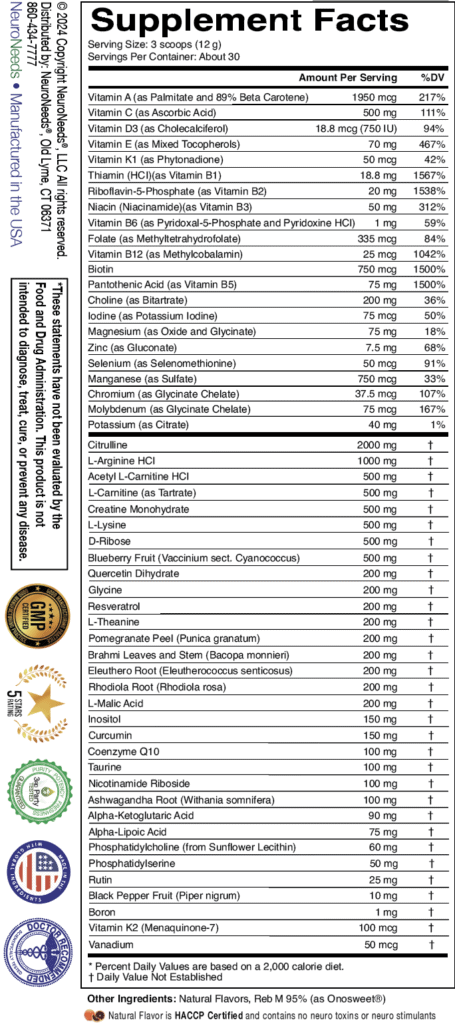
$84
Cobalamin
Cobalamin, also known as vitamin B12, cannot be manufactured by humans and is obtained exclusively from the diet. Cobalamin is an enzyme cofactor for two enzymes in energy metabolism and methylation/folate metabolism. Cobalamin has critical functions in the nervous system, including via the synthesis of myelin, and in the formation of red blood cells. Cobalamin deficiency is fairly common, especially in individuals with vegan-like diets, gastrointestinal conditions, and/or autoimmune disease. Deficiency can result in anemia, functional symptoms (fatigue, weakness, lightheadedness), or neurological features (numbness or tingling, problems walking, psychosis, behavioral changes), which may be irreversible. Cobalamin is often used in the treatment of brain disorders. It is also used to treat elevated levels of blood homocysteine, and as a general “energy” supplement. The form of cobalamin used in most nutritional supplements is cyanocobalamin, although methylcobalamin (the form in ActivNeeds) is preferred due to the lack of need to detoxify the cyanide component. Due to the poor oral bioavailability of cobalamin, the dosage in ActivNeeds is very high. Nonetheless, side effects are unexpected, and even young children tolerate far higher doses.
Cobalamin in ActivNeeds
Cobalamin, in the form of methylcobalamin, is present in ActivNeeds® in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of cobalamin in energy metabolism and the preliminary data regarding its use as a dietary supplement in brain disorders. Side effects are unexpected.
Cobalamin, also known as vitamin B12, is one of the eight B-complex vitamins. Cobalamin cannot be manufactured by humans and is thus a true vitamin, obtained exclusively from the diet.
Cobalamin is an enzyme cofactor for only two human enzymes, yet they are in critical pathways: energy metabolism and methylation/folate metabolism. Among many other functions, some of the more critical requirements for cobalamin are in the function of the nervous system, including via the synthesis of myelin (white matter), and in the formation of red blood cells.
Cobalamin deficiency is fairly common, especially in individuals with diets poor in animal products, gastrointestinal conditions, and/or autoimmune disease. Deficiency might first present as a megaloblastic (large red blood cells) anemia. Functional symptoms are common, including fatigue, weakness, lightheadedness, constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite, heart palpitations with shortness of breath. Neurological features are also common, and may in part be irreversible, including numbness or tingling, problems walking, loss of vision or taste, anxiety, depression, mania, psychosis, memory loss, or behavioral changes.
Multiple studies support the role of cobalamin in the treatment of some brain disorders. Cobalamin, often along with folate and pyridoxine, is sometimes used to treat elevated levels of blood homocysteine, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Although used, its use in cognitive function and dementia have not been substantiated. Cobalamin is a common ingredient in “energy drinks”.
Methylcobalamin and 5-deoxyadenosylcobalamin are the active forms of cobalamin used in human enzymes. The form of cobalamin used in most nutritional supplements is cyanocobalamin. Methylcobalamin, the substrate for methionine synthase, is also available as a supplement, and is preferred due to the lack of need to detoxify the cyanide component, however small, of cyanocobalamin. The body’s ability to absorb cobalamin from the gut is limited by the availability of intrinsic factor, which is the reason that injectable forms of cobalamin are employed in many studies related to autism.
Cobalamin is water-soluble and excessive amounts are excreted by the kidneys, so toxicity is unlikely. Far higher dosages are frequently provided by injection in children with autism. Side effects are rare at usual doses used in oral supplementation.
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a deficiency of this nutrient, but this test often fails to reveal deficiencies that are mild. The preferred test is to measure blood methylmalonate and homocysteine levels, which are elevated even in mild cobalamin deficiency. Decreased brain and/or spinal cord myelination is another sign of potential cobalamin deficiency.
How and Why is Cobalamin Used in ActivNeeds
Cobalamin is added to ActivNeeds in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of cobalamin in energy metabolism, and because of the available data suggesting an important role in brain health. While definitive large double-blind studies have not been performed to date, the multiple studies performed to date, the clinical experience of many physicians, and the generally benign nature of cobalamin supplementation, have convinced many experts to offer cobalamin supplementation to their patients with various brain disorders. Due to the poor oral bioavailability of cobalamin, the dosage in ActivNeeds is very high. Nonetheless, side effects are unexpected, and even young children tolerate far higher doses.
Order ActivNeeds Today
Formulations